Safety Rate
Safety Rate
Cartilage is essential for smooth joint movement and effective shock absorption, but it has a very limited ability to heal once damaged. Injuries, overuse, or early degenerative changes can gradually lead to pain, swelling, and stiffness that affect daily activities. When conventional treatments fail to provide relief, advanced solutions are considered. One such option is ACI cartilage transplant in Chennai, which uses a patient’s own healthy cartilage cells to repair damaged areas. This innovative approach aims to restore joint function, reduce pain, and support long-term mobility.
Meet our experienced team of anaesthesiologists dedicated to your safety and comfort
Our experienced anaesthesiologists are here to ensure your safety and comfort
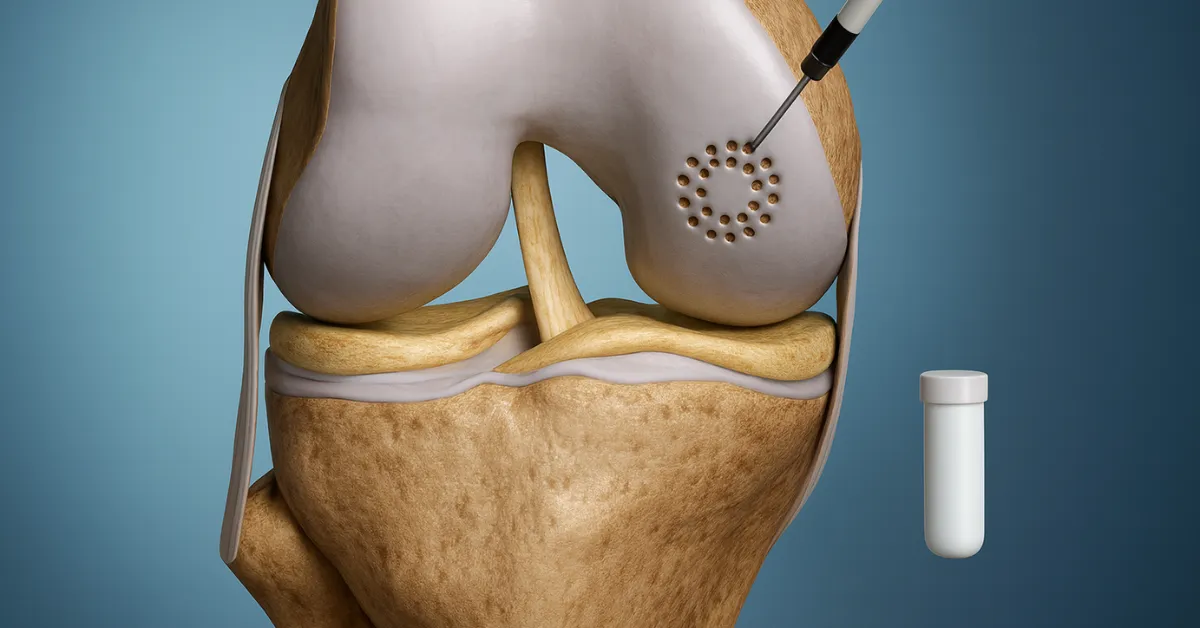
Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation (ACI) is a two-step surgical procedure used to repair damaged articular cartilage, typically in the knee. In the first step, a small sample of healthy cartilage is harvested from the patient. These cartilage cells (chondrocytes) are then cultured in a laboratory to multiply. In the second step, the expanded chondrocytes are implanted into the damaged area of the joint, promoting the growth of new cartilage. ACI is often considered for young, active patients with isolated cartilage defects who wish to avoid joint replacement.
The success rate of ACI varies depending on factors such as the size and location of the cartilage defect, patient age, and adherence to post-operative rehabilitation. Overall, studies indicate that ACI has a high success rate, with approximately 80% to 90% of patients experiencing significant improvement in pain relief and joint function. However, outcomes can differ, and some patients may require revision procedures over time.
The cost of ACI surgery varies widely depending on the country, hospital, and complexity of the procedure. On average, it can range from $15,000 to $40,000 USD, including hospital fees, surgeon charges, and rehabilitation. Additional costs may include diagnostic tests, physiotherapy, and medications. Insurance coverage can reduce out-of-pocket expenses depending on the plan and location.