Safety Rate
Safety Rate
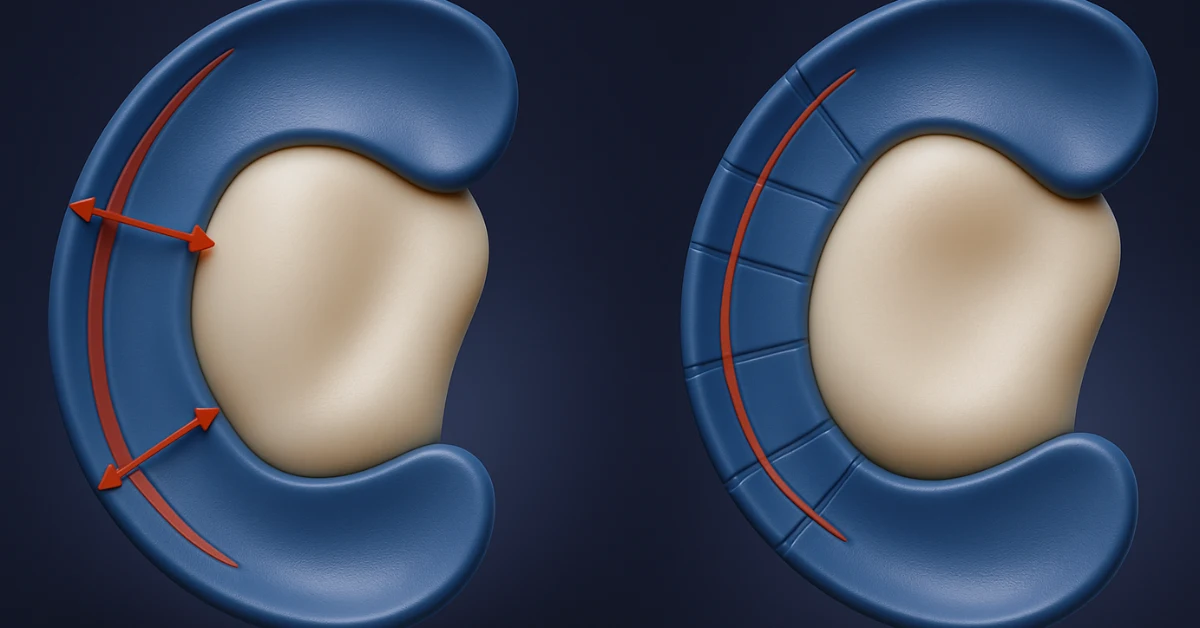
The medial meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage structure on the inner side of the knee that cushions the joint, distributes weight, and provides stability between the thighbone (femur) and shinbone (tibia). When torn, the meniscus loses its ability to protect the knee, leading to pain, swelling, locking, and reduced mobility. These injuries often occur during sports activities, twisting motions, or as part of age-related degeneration.
Rather than removing the damaged tissue, arthroscopic medial meniscal repair surgery in Chennai focuses on restoring the meniscus to its natural form. Preserving the meniscus is crucial—it reduces the risk of arthritis, maintains joint biomechanics, and prolongs long-term knee health.
Meet our experienced team of anaesthesiologists dedicated to your safety and comfort
Our experienced anaesthesiologists are here to ensure your safety and comfort
Arthroscopic repair of the medial meniscus is a minimally invasive procedure that restores the natural cartilage structure in the knee. It helps maintain stability, cushioning, and joint function while preventing arthritis. Arthroscopic medial meniscal repair surgery in Chennai focuses on preserving the meniscus for long-term knee health, improved mobility, and quicker recovery.
Recovery after medial meniscus arthroscopy typically takes 6 to 8 weeks, depending on the severity of the tear and rehabilitation progress. Physiotherapy plays a key role in regaining strength and flexibility. Patients undergoing Arthroscopic medial meniscal repair surgery in Chennai receive personalized rehab plans for safe, effective healing and an active return to daily activities.
Yes, most patients can begin walking with support within a few days after surgery, depending on the repair type. Gradual weight-bearing is introduced under medical supervision. Arthroscopic medial meniscal repair surgery in Chennai ensures minimally invasive care, allowing faster recovery, improved stability, and a smoother return to normal walking and knee function
The cost of arthroscopic medial meniscus repair varies based on hospital facilities, surgeon expertise, and injury complexity. On average, it ranges from ₹90,000 to ₹2,00,000. Patients opting for Arthroscopic medial meniscal repair surgery in Chennai benefit from advanced techniques, skilled orthopedic specialists, and affordable treatment plans ensuring precise repair and faster rehabilitation.