Safety Rate
Safety Rate
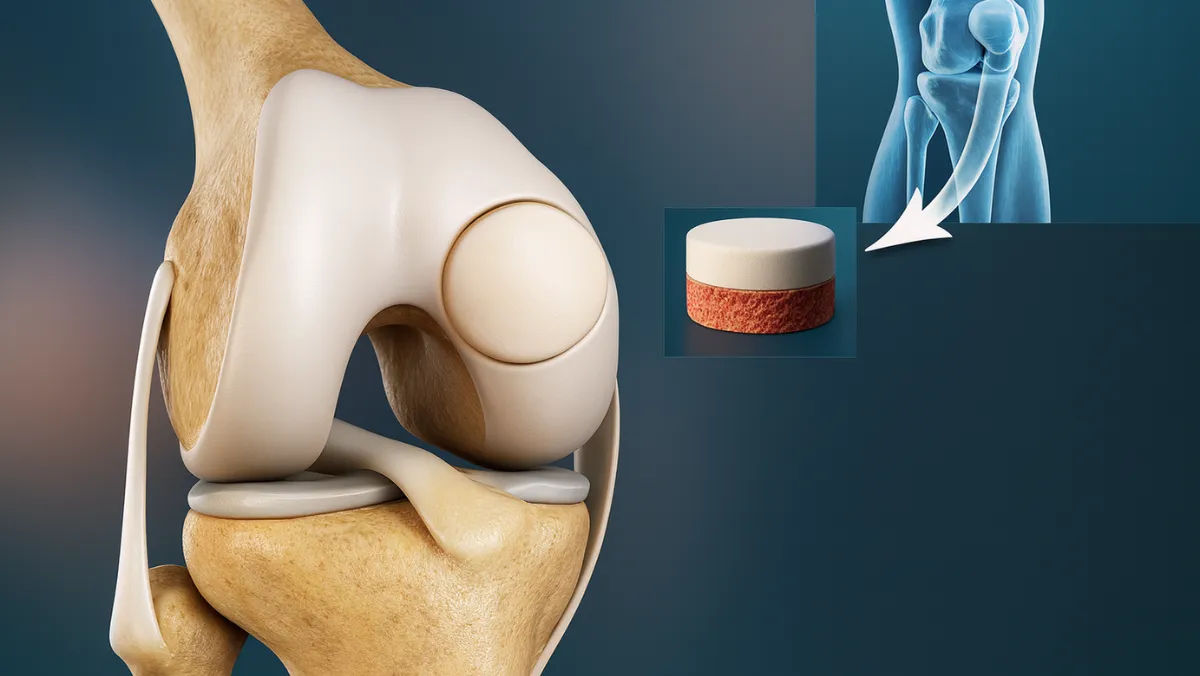
Osteochondritis Dissecans (OCD) is a joint condition where a segment of cartilage, along with a thin layer of underlying bone, becomes loose due to reduced blood flow. This commonly affects the knee joint, particularly the femoral condyle, and can cause pain, swelling, locking, and instability. If untreated, OCD may progress to long-term cartilage damage and early arthritis.
Arthroscopic OCD fixation is a minimally invasive surgical technique that stabilizes the loose fragment and restores the smooth joint surface. Unlike open surgery, arthroscopy uses small incisions and specialized instruments, allowing faster recovery, less scarring, and improved outcomes.
Meet our experienced team of anaesthesiologists dedicated to your safety and comfort
Our experienced anaesthesiologists are here to ensure your safety and comfort
Yes, OCD of the knee can become serious if not treated at the right time. It occurs when a piece of cartilage and underlying bone loosens due to poor blood supply, causing pain, swelling, and joint locking. If ignored, it may lead to cartilage damage and early arthritis. Early diagnosis allows joint-preserving treatment. Arthroscopic OCD fixation surgery in Chennai helps stabilize the loose fragment, relieve symptoms, and protect long-term knee function.
The cost of OCD knee surgery depends on factors such as the severity of the condition, hospital facilities, surgeon expertise, and rehabilitation needs. Minimally invasive arthroscopic procedures are generally more affordable than open surgeries and offer quicker recovery. Chennai provides advanced orthopedic care at competitive pricing compared to many cities. Opting for arthroscopic OCD fixation surgery in Chennai gives patients access to modern treatment options with transparent costs and comprehensive postoperative support.
In surgical terms, OCD refers to treating osteochondritis dissecans by stabilizing or fixing the loose cartilage and bone fragment within the joint. Arthroscopic surgery is commonly used, involving small incisions and specialized instruments to preserve the natural joint surface. This approach reduces pain, limits scarring, and speeds recovery. Arthroscopic OCD fixation surgery in Chennai focuses on restoring joint stability, preventing further damage, and maintaining long-term knee health.