Safety Rate
Safety Rate
Hip fractures can significantly limit movement, especially in older adults, with trochanteric fractures being a common type affecting the upper femur near the hip. These injuries often occur due to falls, accidents, or weakened bones caused by osteoporosis. To restore strength and stability, PFN fixation of fracture treatment in Chennai is widely used as an advanced surgical option. This minimally invasive technique provides strong internal support, promotes faster bone healing, and helps patients regain mobility sooner. Early rehabilitation further improves functional recovery and independence.
Meet our experienced team of anaesthesiologists dedicated to your safety and comfort
Our experienced anaesthesiologists are here to ensure your safety and comfort
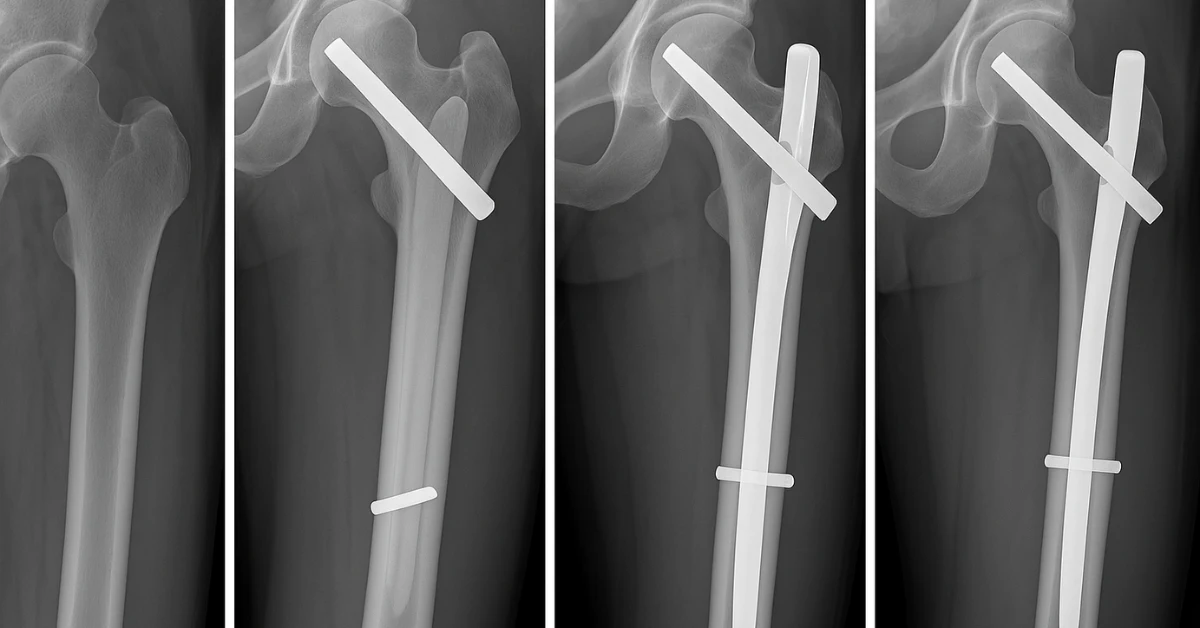
PFN (Proximal Femoral Nail) fixation is a surgical procedure used to treat fractures of the proximal femur, particularly intertrochanteric and subtrochanteric fractures. It involves inserting a metal nail into the femur’s marrow cavity, which is secured with screws to stabilize the bone. PFN fixation allows early mobilization, reduces complications, and helps in faster fracture healing compared to traditional methods.
The PFN method is a minimally invasive orthopedic technique where a specially designed intramedullary nail is inserted into the femur to stabilize fractures near the hip. The nail is locked with screws at the proximal and distal ends, providing strong internal support. This method maintains alignment, supports weight-bearing early, and minimizes soft tissue damage and blood loss during surgery.
PNF (Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation) is a rehabilitation technique used to improve flexibility, strength, and coordination. The four main types of PNF techniques are:
Hold-Relax – stretching the muscle, then isometric contraction, followed by further stretching.
Contract-Relax – contracting the muscle against resistance, then relaxing and stretching.
Hold-Relax with Agonist Contraction (HR-AC) – combining isometric hold and active movement of the opposing muscle.
Rhythmic Initiation – gradually moving from passive to active-assisted and then active movements to improve control and coordination.