Injuries around the knee are quite common, especially among active individuals or those engaged in physical work. A fall, sudden twist, or overuse can strain the delicate tissues that hold the knee together. When the muscles, tendons, or ligaments are stretched or torn, discomfort and swelling can quickly set in. A knee soft tissue injury can occur from something as simple as missing a step or landing awkwardly during sports. Identifying the signs early and getting proper care helps avoid long-term weakness or instability.
Understanding Soft Tissue Injuries
Soft tissue injuries involve damage to the muscles, tendons, or ligaments that support joint movement and stability. These tissues act as cushions and connectors, allowing the body to bend, stretch, and move smoothly. In many cases, a knee soft tissue injury results from repetitive strain or sudden trauma that exceeds the body’s normal range of motion. For instance, runners or athletes who train on hard surfaces often experience such injuries due to continuous stress on their knees. With timely rest, physical therapy, and guided exercises, most soft tissue injuries heal well without lasting complications.
Different Types of Soft Tissue Injuries
Knee soft tissue injuries vary in severity and can affect multiple structures around the knee joint. Below are the common types:
- Strains: These occur when muscles or tendons are overstretched or torn, often during lifting or sudden movement. They cause sharp pain, stiffness, and limited mobility.
- Sprains: These affect the ligaments connecting bones. A knee sprain often leads to swelling, bruising, and joint instability.
- Contusions: Also known as bruises, they happen due to direct impact or a fall, causing tenderness and discoloration under the skin.
- Tendonitis (affects soft tissue knee injury recovery time): Inflammation of the tendons caused by repetitive stress or overuse. It can extend recovery and require rest and therapy.
- Bursitis: Occurs when small fluid-filled sacs (bursae) that cushion the knee become irritated, leading to swelling and discomfort.
Understanding the specific injury type helps determine the right approach to treatment and recovery.
How Severe Can a Soft Tissue Injury Be?
The seriousness of a soft tissue injury depends on how much the tissues are damaged and how soon treatment begins. Ignoring pain can lead to chronic issues or further tearing.
- Mild Injuries: These include minor strains or small tears that typically heal with rest, ice, and gentle stretching.
- Moderate Injuries: These involve partial tears that restrict movement and cause lingering pain. Rehabilitation exercises and physiotherapy are usually required.
- Severe Injuries: When soft tissue damage is extensive, surgical repair or long-term therapy may be necessary. In such cases, a knee soft tissue injury should be evaluated immediately to avoid long-term complications. Seeking medical attention early ensures faster recovery and reduces the risk of joint instability.
Common Symptoms and Causes of Soft Tissue Damage
Early soft tissue knee injury treatment such as rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) can help relieve discomfort and promote healing. Recognizing symptoms early can make treatment more effective and shorten recovery time.
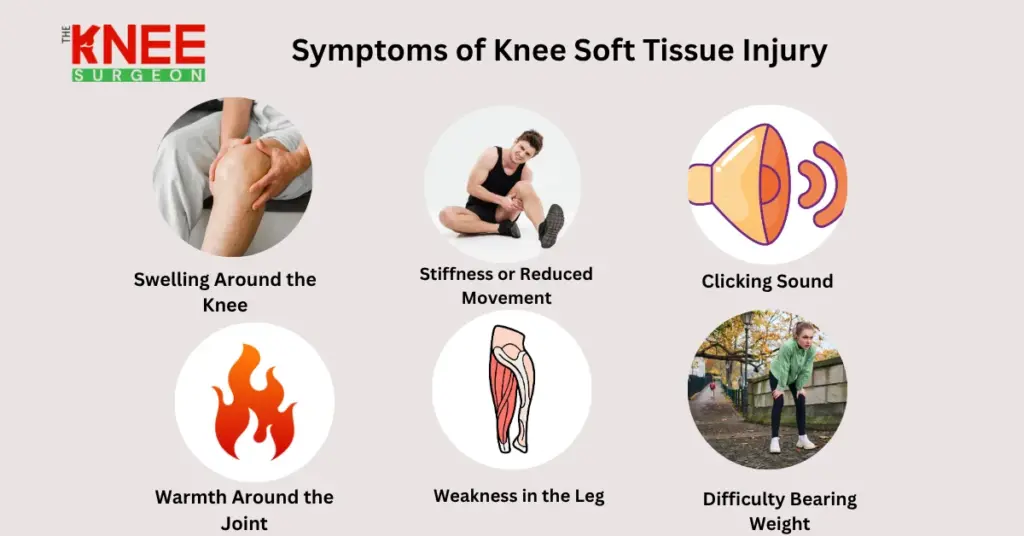
Common Symptoms
- Pain that worsens when moving or applying pressure
- Swelling or bruising around the affected knee
- Limited range of motion or stiffness
- Weakness and tenderness in the joint
Common Causes
- Overuse during sports or repetitive physical activity
- Sudden falls, twists, or awkward movements
- Poor warm-up or muscle fatigue
- Incorrect posture or imbalance in muscle strength
In recurring cases, physiotherapy and strengthening exercises are key to full recovery from a knee soft tissue injury.
Possible Complications from Soft Tissue Injuries
If not managed correctly, soft tissue injuries can lead to lasting problems that affect daily movement and flexibility. The severity and care taken can influence soft tissue knee injury recovery time significantly.
Common Complications
- Chronic Pain and Swelling: Occur when tissues don’t heal properly or inflammation persists.
- Joint Instability: Damaged ligaments may weaken the knee, increasing the risk of re-injury.
- Muscle Weakness: Long periods of rest without strengthening exercises can reduce stability.
- Scar Tissue Formation: Improper healing may cause stiffness and reduced flexibility.
Timely treatment and guided rehabilitation are essential to prevent these complications and ensure strong recovery.
Diagnosis of Soft Tissue Injuries
Proper diagnosis helps determine the extent of soft tissue damage and guides the best course of treatment.
Physical Examination: Doctors check for tenderness, swelling, and mobility while asking about the cause and timing of pain.
Imaging Tests:
- X-rays rule out bone fractures.
- MRI scans give detailed images of torn ligaments or inflamed tendons.
- Ultrasound helps identify minor strains or fluid buildup.
Functional Testing: Patients may be asked to perform gentle movements to assess joint stability and flexibility. Detecting a knee soft tissue injury early allows for a personalized treatment plan that supports complete recovery.
Recovery Time for Soft Tissue Injury Healing
Following a dedicated soft tissue knee injury treatment plan that includes rest, ice, compression, and gradual activity can shorten healing time.The healing period depends on the severity of injury and how consistently treatment is followed.
Typical Healing Durations
- Mild injuries: 2–3 weeks with rest and light exercise
- Moderate injuries: 4–6 weeks with physiotherapy
- Severe injuries: Up to 3 months or more with rehabilitation
For example, a knee soft tissue injury often improves faster when supported by muscle-strengthening routines and proper diet. Consistency with therapy and patience are key to regaining full joint mobility and stability.
Tips to Prevent Soft Tissue Injuries
Prevention is always better than prolonged recovery. Maintaining flexibility, strength, and proper posture helps protect your joints.
Effective Prevention Tips
- Always warm up before physical activity to loosen muscles.
- Strengthen the muscles supporting your knees and ankles.
- Use correct posture during workouts or lifting.
- Take rest days to prevent overuse, as fatigue increases soft tissue knee injury recovery time.
Simple daily habits like stretching, balanced exercise, and hydration go a long way in preventing a knee soft tissue injury and keeping your joints healthy.
Conclusion
Recovering from a knee soft tissue injury requires patience, proper care, and medical supervision. Early diagnosis and a structured recovery plan help restore movement and reduce the risk of recurring pain. For expert guidance and advanced care, consult Dr. Madan mohan Reddy, the best orthopedic and knee surgeon in Chennai. With his experience and precise approach to joint healing, patients can expect faster recovery, stronger knees, and lasting comfort in every step.
Read more: Knee Pain in Winter







